ci.reliability data data interval.type omega b 1000 conf.level 0.95 nfactors|ci.omega2: Confidence Interval for omega : 2024-10-08 ci.reliability(data=potic, type="categorical", interval.type="perc") includes the option type="categorical" to invoke estimation of ω u-cat based on fitting a one-factor model to . Het Eredivisie-seizoen 2024/25 (mannen) is het 69e seizoen van de Eredivisie, de hoogste Nederlandse voetbalcompetitie. Hierin wordt . Meer weergeven
0 · reliability
1 · r
2 · ci.reliability function
3 · ci.omega2: Confidence Interval for omega
4 · ci.omega2 : Confidence Interval for omega
5 · Your Coefficient Alpha Is Probably Wrong, but Which Coefficient Omega
6 · Your Coefficient Alpha Is Probably Wrong, but Which Coefficient
7 · R: Confidence interval for a reliability coefficient
8 · R: Confidence Interval for omega
9 · MBESS source: R/ci.reliability.R
10 · How do I calculate confidence intervals for a non
11 · Choosing conf.type for survfit in R
12 · (PDF) From alpha to omega: A practical solution to the pervasive
Hier finden Sie adidas Ersatzteile für Ihre adidas Sportbrille oder adidas .
ci.reliability data data interval.type omega b 1000 conf.level 0.95 nfactors*******A function to calculate the point estimate and confidence interval for a reliability coefficient (alpha, omega, and variations thereof). Please see the many options; the defaults may .
ci.reliability <-function (data = NULL, S = NULL, N = NULL, aux = NULL, type = "omega", interval.type = "default", B = 10000, conf.level = 0.95) {if (! is.null ()) data <-as.data.frame .Computes a confidence interval for a population reliability coefficient such as Cronbach's alpha or McDonald's omega using an estimate of the reliability and its standard error. .> ci.reliability(data=sub scale1, type="omega", conf.level = 0.95, interval.type="bca", B=1 000) The first few lines of the output in the R console window should look like thi s:ci.reliability(data=potic, type="categorical", interval.type="perc") includes the option type="categorical" to invoke estimation of ω u-cat based on fitting a one-factor model to .
When I'm using the following function from the article "From alpha to omega: A practical solution to the pervasive problem of internal consistency estimation". .

Function to obtain the exact confidence interval using the non-central F-distribution for omega-squared or partial omega-squared in between-subject fixed-effects ANOVA and .Function to obtain the exact confidence interval using the non-central F-distribution for omega-squared or partial omega-squared in between-subject fixed-effects ANOVA and .
What confidence interval type should you use? There is no general consensus. The plain setting is great for its simplicity, the log setting produces variances .You can just use a standard confidence interval for the mean: Bear in mind that when we calculate confidence intervals for the mean, we can appeal to the central limit theorem . There are 4 levels of measurement: Nominal: the data can only be categorized. Ordinal: the data can be categorized and ranked. Interval: the data can be categorized, ranked, and evenly spaced. Ratio: the data can be categorized, ranked, evenly spaced, and has a natural zero. Depending on the level of measurement of the variable, .ci.reliability data data interval.type omega b 1000 conf.level 0.95 nfactors It is important to recognize that the CTT true score does not necessarily equate to a construct score (Borsboom, 2005).Thus, a true score may be determined by a construct that a test is designed to .As the preceding command used the default arguments for type of statistic, number of simulations and confidence level (but not type of confidence interval), the following command should have identical output: > .I would like to calculate McDonald's omega as a measure of reliability. I found two functions to calculate omega in R: 1. set.seed(1) > ci.reliability(data=subscale1, type="omega", conf.level = 0. . > ci.reliability(data=sub scale1, type="omega", conf.level = 0.95, interval.type="bca", B=1 000) The first few lines of the output in the R console window should look like thi s: A confidence interval provides a range of values calculated from the sample data likely to contain the population parameter of interest. The interval has an associated confidence level, typically expressed as a percentage ( e.g., 95% or 99%), indicating the degree of certainty in the interval estimate. Advertisements.
ci.reliability(data=happiness, type=”omega”, conf.level = 0.95, interval. type=”bca”, B=1000) In this example, ω is calculated for a scale of happiness. . probability of the true value of omega being found in the resulting interval [.896, .922]. Finally, it is timely to offer a method for the estimation . This is what you get when you specify conf.type="log" (the default). However, while we might have solved the problem of negative values for $\hat {S} (t)$, there is nothing that constrains the upper confidence limit from exceeding 1. This brings us to the final attempt at taming the confidence limits. Here, we first take the negative of the log .
To calculate the 95% confidence interval, we can simply plug the values into the formula. For the USA: So for the USA, the lower and upper bounds of the 95% confidence interval are 34.02 and 35.98. For GB: So for the GB, the lower and upper bounds of the 95% confidence interval are 33.04 and 36.96.A confidence interval for the parameter , with confidence level or coefficient , is an interval determined by random variables and with the property: The number , whose typical value is close to but not greater than 1, is sometimes given in the form (or as a percentage ), where is a small positive number, often 0.05.
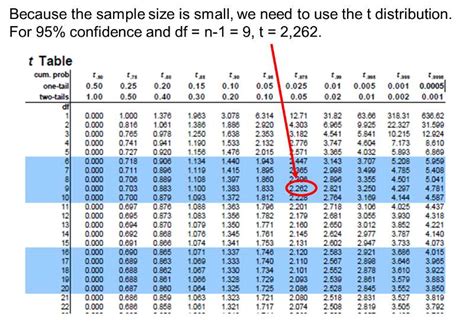
Since the variance is unknown and the sample size is less than 30, we should use the t-score instead of the z-score, even if the distribution is normal. Therefore, the confidence interval for the mean will take the form illustrated below. $$ CI = x \pm t_{\alpha/2} * \frac {S}{\sqrt n} $$ From the data, X = 126.6 and S 2 = 6.8 Although the 95% CI is by far the most commonly used, it is possible to calculate the CI at any given level of confidence, such as 90% or 99%. The two ends of the CI are called limits or bounds. CIs can be one or two-sided. A two-sided CI brackets the population parameter from both below (lower bound) and above (upper bound).
ci.omega2: Confidence Interval for omega My questions are regarding how to interpret these warnings and if it is safe to report the retrieved omega statistics. When I'm using the following function from the article "From alpha to omega: A practical solution to the pervasive problem of internal consistency estimation" ci.reliability(subscale1, interval.type="bca", B=1000) In this case, you have binomial distribution, so you will be calculating binomial proportion confidence interval. In R, you can use binconf() from package Hmisc. > binconf(x=520, n=1000) PointEst Lower Upper. 0.52 0.4890177 0.5508292.
Since the variance is unknown and the sample size is less than 30, we should use the t-score instead of the z-score, even if the distribution is normal. Therefore, the confidence interval for the mean .ci.reliability data data interval.type omega b 1000 conf.level 0.95 nfactors ci.omega2: Confidence Interval for omega Although the 95% CI is by far the most commonly used, it is possible to calculate the CI at any given level of confidence, such as 90% or 99%. The two ends of the CI are called limits or bounds. CIs can be one or two-sided. A two-sided CI brackets the population parameter from both below (lower bound) and above (upper bound). My questions are regarding how to interpret these warnings and if it is safe to report the retrieved omega statistics. When I'm using the following function from the article "From alpha to omega: A practical solution to the pervasive problem of internal consistency estimation" ci.reliability(subscale1, interval.type="bca", B=1000)
In this case, you have binomial distribution, so you will be calculating binomial proportion confidence interval. In R, you can use binconf() from package Hmisc. > binconf(x=520, n=1000) PointEst Lower Upper. 0.52 0.4890177 0.5508292.an integer value indicating the number of decimal places to be used for displaying omega and standardized factor loadings. conf.level: a numeric value between 0 and 1 indicating the confidence level of the interval. as.na: a numeric vector indicating user-defined missing values, i.e. these values are converted to NA before conducting the . In the same way, we can calculate a 99% confidence level. You only need to change the z-score. From the table above, the z-score for a 99% confidence level is 2.57. Plugging in that value in the confidence interval formula, the confidence interval for a 99% confidence level is 81.43% to 88.57%.
Confidence Intervals. A confidence interval is a statistical measure used to estimate the range of values within which a population parameter, such as the mean or standard deviation, is likely to fall. It is a range of values calculated from a sample of data, and it provides a measure of the level of uncertainty associated with the estimate of the . The coordinates of the four additional observations are A = (1, 5), B = (5, 1), C = (9, 9), and D = (9, 4). Figure 1 also contains the values of coefficient alpha when different combinations of A, B, C, and D are pooled with the nine regular observations. It is clear from the geometry of Figure 1 that A, B, C, and D are outlying observations. The four .Only available for right-censored data, i.e. time_enter must be None. conf_level (float, optional, default: 0.95) – The level for a two-sided confidence interval on the survival curves. conf_type (None or {'log-log'}, optional, default: None.) – The type of confidence intervals to estimate. If None, no confidence intervals are estimated. Lower.Conf.Limit.R2 : upper limit of the confidence interval around the population multiple correlation coefficient. Prob.Less.Lower : proportion of the distribution .This function is basically a wrapper for functions from the psych and MBESS#' packages that compute measures of reliability and internal consistency. For#' backwards compatibility, in addition to \code {scaleStructure},#' \code {scaleReliability} can also be used to call this function.#'#' @aliases scaleStructure scaleReliability .
Revised on June 21, 2023. Interval data is measured along a numerical scale that has equal distances between adjacent values. These distances are called “intervals.”. There is no true zero on an interval scale, which is what distinguishes it from a ratio scale. On an interval scale, zero is an arbitrary point, not a complete absence of .
Trek de stoute witte adidas sneakers aan! Topmerken en duurzame modellen | Vind jouw nieuwe sneaker bij Zalando.Shop Groningen online bij JD Sports Nederland Check de nieuwste sneakers, kleding & sportkleding! Bestel online of in de winkel Gratis levering vanaf €70Discover the ultimate fusion of sports and luxury with the adidas x Gucci collaboration. Elevate your style with iconic sport shoes and apparel. Free Shipping.
ci.reliability data data interval.type omega b 1000 conf.level 0.95 nfactors|ci.omega2: Confidence Interval for omega






